Appendix: a reference guide to orders
Summary of the diagnostic features of the three non-hexapod orders and the 30 orders of Insecta.
Protura(proturans)
| Very small, wingless, eyeless, without antennae, entognathous (mouthparts within folds of head), fore legs held forward, thoracic segments like those of abdomen, legs five-segmented, adult abdomen 12-segmented without cerci; immature stages like small adult but with fewer abdominal segments. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.2 |
Collembola(springtails)
| Small, wingless, mouthparts entognathous, antennae present, thoracic segments like those of abdomen, legs four-segmented, abdomen six-segmented with sucker-like ventral tube and forked jumping organ, without cerci; immature stages like small adult, with constant segment number. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.2 |
Diplura(diplurans)
| Small to medium, wingless, eyeless, entognathous, long antennae like string of beads, thoracic segments like those of abdomen, legs five-segmented, abdomen 10-segmented, some with small protrusions, terminal cerci filiform to forceps-like; immature stages like small adult. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.2 |
Archaeognatha(bristletails)
| Medium, wingless, with humped thorax, hypognathous (mouthparts directed downwards), large compound eyes in near contact, some abdominal segments with paired styles and vesicles, with three «tails» — paired cerci shorter than single median caudal appendage; immature stages like small adult. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.3 |
Zygentoma or Thysanura(silverfish)
| Medium, flattened, silvery-scaled, wingless, hypognathous to prognathous (mouthparts directed downwards to forwards), compound eyes small, widely separated or absent, some abdominal segments with ventral styles, with three «tails» — paired cerci nearly as long as median caudal appendage; immature stages like small adult. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.3 |
Ephemeroptera(mayflies)
| Small to large, winged with large triangular fore wings and smaller hind wings, mouthparts reduced, compound eyes large, short filiform antennae, abdomen slender compared to stout thorax, with three «tails» — paired cerci often as long as median caudal appendage; immature stages (nymphs) aquatic, with three «tails» and plate-like abdominal gills, penultimate instar a winged subimago. | Chapters 7, 10 Box 10.1 |
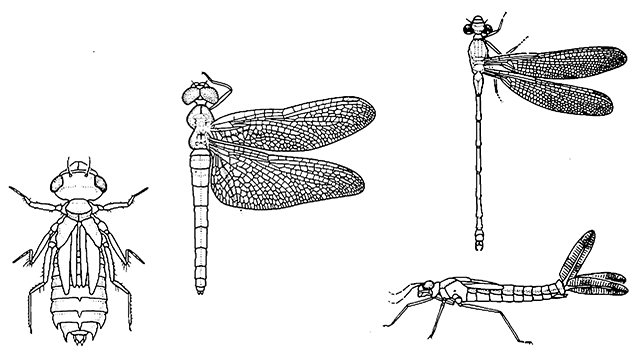
Odonata(dragonflies, damselflies)
| Medium to large, winged, with fore and hind wings equal (Zygoptera) or hind wings wider than fore wings (Anisoptera), head mobile, with large compound eyes separated (Zygoptera) or nearly in contact (Anisoptera), mouthparts mandibulate, antennae short, thorax stout, abdomen slender; immature stages (nymphs) aquatic, stout or narrow, with extensible labial «mask», terminal or rectal gills. | Chapters 7, 10 |
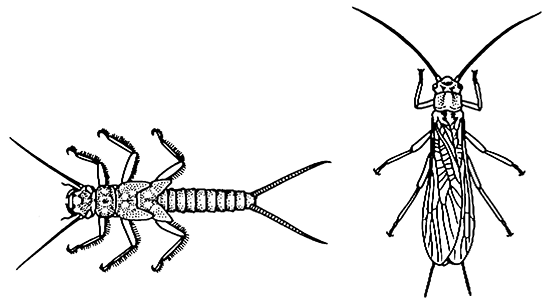
Plecoptera(stoneflies)
| Medium, with fore and hind wings nearly equal (subequal) in size, at rest wings partly wrap abdomen and extend beyond abdominal apex but wing reduction frequent, legs weak, abdomen soft with filamentous cerci; immature stages (nymphs) aquatic resembling wingless adults, often with gills on abdomen. | Chapters 7, 10 Box 10.3 |
Isoptera(termites or “white ants”)
| Small to medium, mandibulate (with variable mouthpart development in different castes), antennae long, compound eyes often reduced, in winged forms fore and hind wings usually similar, often with reduced venation, body terminates in one- to five-segmented cerci; immature stages morphologically variable (polymorphic) according to caste. | Chapters 7, 12 Box 12.3 |
Blattodea(roaches, cockroaches)
| Small to large, dorsoventrally flattened, hypognathous, compound eyes well developed (except in cave dwellers), prothorax large and shield-like (may cover head), fore wings form leathery tegmina, protecting large hind wings, large anal lobe on hind wing, coxae large and abutting ventrally, cerci usually multisegmented; immature stages (nymphs) like small adults. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.8 |
Mantodea(mantids)
| Moderate to large, head small, mobile, and triangular, compound eyes large and separated, thorax narrow, fore wings form tegmina, hind wings broad, fore legs predatory (raptorial), mid and hind legs elongate; immature stages (nymphs) resemble small adults. | Chapters 7, 13 |
Grylloblattodea(rock crawlers or ice crawlers)
| Medium, soft-bodied, elongate, pale, wingless and often eyeless, prognathous, with stout coxae on legs adapted for running, cerci five- to nine-segmented, female with short ovipositor; immature stages (nymphs) like small pale adults. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.4 |
Mantophasmatodea(heel walkers)
| Small to medium, somewhat cylindrical, hypognathous, antennae long, multisegmented, compound eyes large, fore and mid legs raptorial, wings absent, cerci small in female, prominent in male; immature stages (nymphs) resemble small adults. | Chapters 7, 13 Box 13.3 |
Phasmatodea(phasmatids, phasmids, stickinsects or walking sticks)
| Medium to large, cylindrical stick-like or flattened leaf-like, prognathous, mandibulate, compound eyes small and laterally placed, fore wings form leathery tegmina, hind wings broad with toughened fore margin, legs elongate for walking, cerci one-segmented; immature stages (nymphs) like small adults. | Chapters 7, 11, 14 Box 11.6 |
Embiidina or Embioptera(embiids, webspinners)
| Small to medium, elongate, cylindrical, prognathous, compound eyes kidneyshaped, wingless in all females, some males with soft, flexible wings, legs short, basal fore tarsus swollen with silk gland, cerci twosegmented; immature stages like small adults. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.5 |
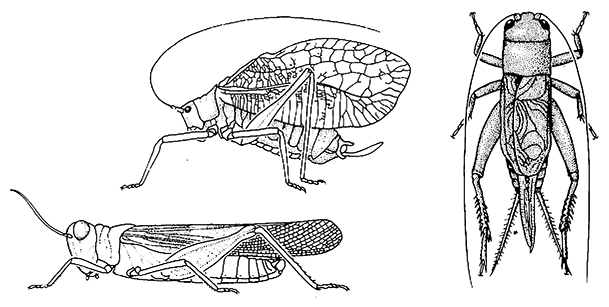
Orthoptera(grasshoppers, locusts, katydids, crickets)
| Medium to large, hypognathous, usually winged, fore wings forming leathery tegmina, hind wings broad, at rest pleated beneath tegmina, pronotum curved over pleura, hind legs often enlarged for jumping, cerci onesegmented; immature stages (nymphs) like small adults. | Chapters 5, 7, 11 |
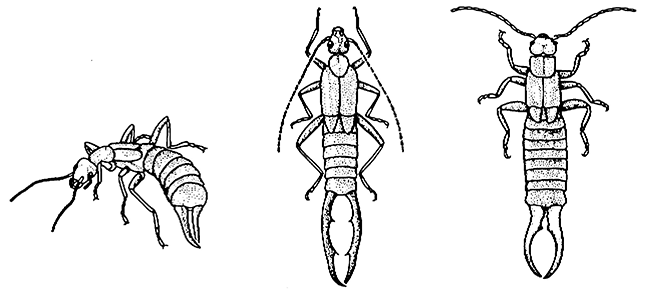
Dermaptera(earwigs)
| Small to medium, elongate and flattened, prognathous, antennae short to moderate, legs short, if wings present the fore wings are small leathery tegmina, hind wings semicircular, abdomen with overlapping terga, cerci modified as forceps; immature stages (nymphs) resemble small adults. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.7 |
Zoraptera(zorapterans)
| Small, termite-like, hypognathous, winged species with eyes and ocelli, wingless species lack either, if winged then wings with simple venation and readily shed, coxae welldeveloped, abdomen 11-segmented, short and swollen; immature stages (nymphs) resemble small adults. | Chapters 7, 9 Box 9.6 |
Psocoptera(psocids, or barklice, booklice)
| Small to medium, head large and mobile, chewing mouthparts asymmetrical, compound eyes large, antennae long and slender, wings often reduced or absent, if present venation simple, coupled in flight, held roof-like at rest, cerci absent; immature stages (nymphs) like small adults. | Chapters 7, 11 Box 11.9 |
Phthiraptera(lice)
| Small, dorsoventrally flattened, wingless ectoparasites, mouthparts mandibulate or beak-like, compound eyes small or absent, antennae either in grooves or extended, legs stout with strong claw(s) for grasping host hair or feathers; immature stages (nymphs) like small, pale adults. | Chapters 7, 13, 15 Box 15.3 |
Thysanoptera(thrips)
| Small, slender, hypognathous with a feeding tube formed from three stylets — the maxillary laciniae plus the left mandible, with or without wings, if present wings subequal, strap-like, with long fringe; immature stages like small adults. | Chapters 7, 11 Box 11.7 |
Hemiptera(bugs, cicadas, plant- and leafhoppers, aphids, psyllids, scale insects, whiteflies, etc.)
| Small to large, mouthpart stylets lying in proboscis (or rostrum) directed posteriorly at rest, without palps, fore wings may be thickened to form hemelytra (Heteroptera), or membranous; wing reduction or absence is common; immature stages (nymphs) usually resemble small adults. | Chapters 7, 9, 10, 11 Boxes 3.3, 5.5, 9.1, 10.6, 11.2, 11.8, 14.2, 16.1, 16.2, 16.4 |
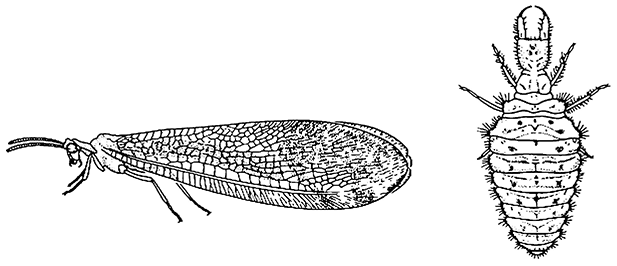
Neuroptera(lacewings, antlions)
| Medium, compound eyes large and separated, mandibulate, antennae multisegmented, prothorax often larger than meso- and metathorax, wings held roof-like over abdomen at rest, fore and hind wings subequal with numerous cross-veins and distal «twigging» of veins, without anal fold; immature stages (larvae) predominantly terrestrial, prognathous, with slender mandibles and maxillae usually forming piercing/sucking mouthparts, with jointed legs only on thorax, lacking abdominal gills. | Chapters 7, 13 |
Megaloptera(alderflies, dobsonflies, fishflies)
| Medium to large, compound eyes large and separated, prognathous, mandibulate, antennae multisegmented, prothorax only slightly longer than meso- and metathorax, fore and hind wings subequal with anal fold in hind wing; immature stages (larvae) aquatic, prognathous, with stout mandibles, jointed legs only on thorax, with lateral abdominal gills. | Chapters 7, 13 |
Raphidioptera(snakeflies)
| Medium, prognathous, mandibulate, antennae multisegmented, compound eyes large and separated, prothorax much longer than mesoand metathorax, fore wings rather longer than otherwise similar hind wings, without anal fold; immature stages (larvae) terrestrial, prognathous with jointed legs only on thorax, without abdominal gills. | Chapters 7, 13 Box 13.4 |
Coleoptera(beetles)
| Small to large, often sturdy and compact, heavily sclerotized or armored, mandibulate, with fore wings modified as rigid elytra covering folded hind wings at rest, legs variously modified, often with claws and adhesive structures; immature stages (larvae) terrestrial or aquatic with sclerotized head capsule, opposable mandibles and usually fivesegmented thoracic legs, without abdominal legs or labial silk glands. | Chapters 7, 10, 11 |
Strepsiptera(strepsipterans)
| Small, aberrant endoparasites; male with large head, bulging eyes with few facets, antennae with fan-shaped branches, fore wings stubby, without veins, hind wings fan-shaped with few veins; female larviform, wingless, retained in host; immature stages (larvae) initially a triungulin with three pairs of thoracic legs, later maggot-like without mouthparts. | Chapters 7, 13 Box 13.6 |
Diptera(flies)
| Small to medium, wings restricted to mesothorax, metathorax with balancing organs (halteres), mouthparts vary from nonfunctional, to biting and sucking; immature stages (larvae, maggots) variable, without jointed legs, with sclerotized head capsule or variably reduced ultimately to remnant mouth hooks. | Chapters 7, 10, 15 |
Mecoptera(scorpionflies, hangingflies)
| Medium, hypognathous with elongate rostrum formed from slender, serrate mandibles and maxillae and elongate labium, fore and hind wings narrow and subequal, legs raptorial; immature stages (larvae) mostly terrestrial, with heavily sclerotized head capsule, compound eyes, short, jointed thoracic legs, abdomen usually with prolegs. | Chapters 5, 7, 13 |
Siphonaptera(fleas)
| Small, highly modified, laterally compressed ectoparasites, mouthparts piercing and sucking, without mandibles, antennae lying in grooves, body with many backwardly directed setae and spines, some as combs, legs strong, terminating in strong claws for grasping host; immature stages (larvae) terrestrial, apodous (legless), with distinct head capsule. | Chapters 7, 15 Box 15.4 |
Trichoptera(caddisflies)
| Small to large, with long, multisegmented antennae, reduced mouthparts (no proboscis) but well-developed maxillary and labial palps, hairy (or rarely scaly) wings, lacking discal cell and with fore wing anal veins looped (cf. Lepidoptera); immature stages (larvae) aquatic, often case-bearing, but many free-living, with three pairs of segmented thoracic legs and lacking abdominal prolegs. | Chapters 7, 10 Box 10.4 |
Lepidoptera(moths, butterflies)
| Small to large, hypognathous, nearly all with long coiled proboscis, antennae multisegmented and often comb-like (pectinate), clubbed in butterflies, wings with double layer of scales and large cells including the discal; immature stages (larvae, caterpillars) with sclerotized mandibulate head, labial spinnerets producing silk, jointed legs on thorax and some abdominal prolegs. | Chapters 7, 11, 14 |
Hymenoptera(sawflies, wasps, ants, bees)
| Minute to large, mouthparts mandibulate to sucking and chewing, antennae multisegmented often long and held forward, thorax either three-segmented or forms a mesosoma by incorporation of first abdominal segment in which case the abdomen is petiolate (waisted), wings with simple venation, fore and hind wings coupled together by hooks on hind wing; immature stages (larvae) very variable, many lack legs completely, all have distinct mandibles even if head is reduced. | Chapters 7, 12, 13, 14 |