Figures 7.1
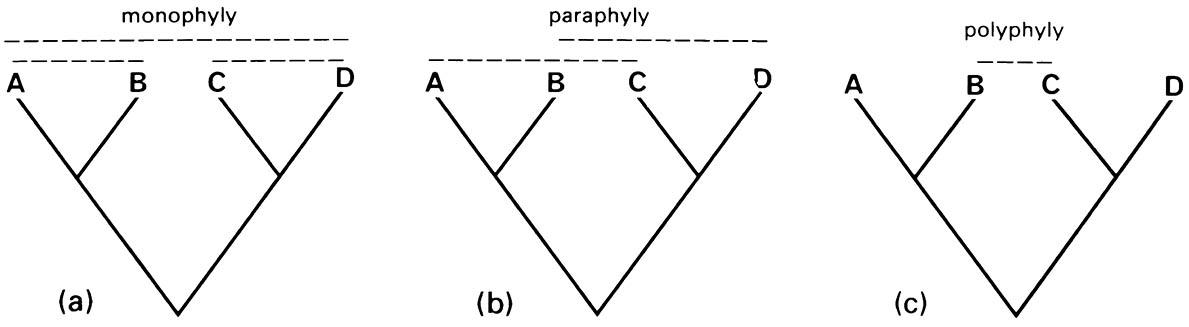
Figures 7.1. A cladogram showing the relationships of four species, A, B, C, and D, and examples of (a) the three monophyletic groups, (b) two of the four possible (ABC, ABD, ACD, BCD) paraphyletic groups, and (c) one of the four possible (AC, AD, BC, an d BD) polyphyletic groups that could be recognized based on this cladogram.

